之前我们已经了解了shuffle writer的详细过程,那么生成文件后会发生什么呢?以及它们是如何被读取呢?读取是内存的操作吗?这些问题也随之产生,那么今天我们将先来了解了shuffle reader的细枝末节。
在文章Spark Shuffle概述中我们已经知道,在ShuffleManager中不仅定义了getWriter来获取map writer的实现方式, 同时还定义了getReader来获取读取shuffle文件的实现方式。
在Spark中调用有两个调用getReader的抽象类的重要实现,分别是ShuffledRDD和ShuffleRowRDD。前者是与RDD API交互,后面一个是DataSet Api的交互实现。在Spark 3.0后其核心已经变成了Spark SQL,所以我们重点从ShuffleRowRDD调用getReader开始讲起。
从ShuffleRowRDD开始
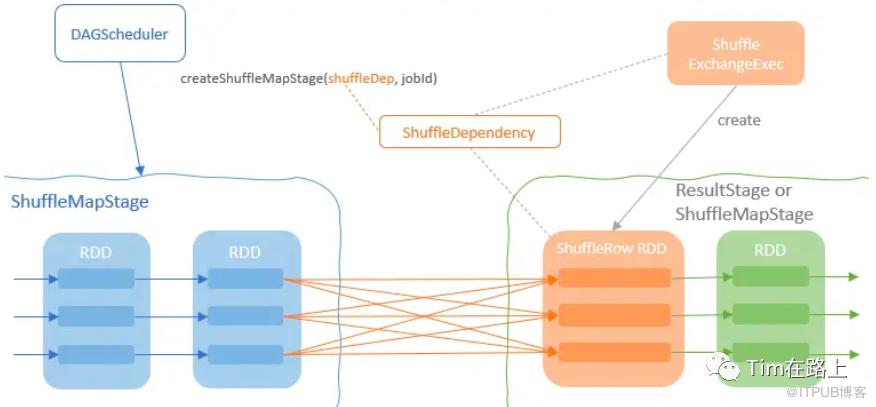
ShuffleRowRDD主要是被ShuffleExchangeExec调用。
这里简单介绍下ShuffleExchangeExec操作算子。ShuffleExchangeExec主要负责两件事:首先,准备ShuffleDependency,它根据父节点所需的分区方案对子节点的输出行进行分区。其次,添加一个ShuffleRowRDD并指定准备好的ShuffleDependency作为此RDD的依赖项。
1class ShuffledRowRDD(
2 var dependency: ShuffleDependency[Int, InternalRow, InternalRow],
3 metrics: Map[String, SQLMetric],
4 partitionSpecs: Array[ShufflePartitionSpec])
5 extends RDD[InternalRow](dependency.rdd.context,Nil)
ShuffleRowRDD继承自RDD[InternalRow], 同时内部维护着三个参数,分别是dependency,metrics和partitionSpecs。dependency封装着shuffleId , shuffleHandle, numPartitions 可以基于其判断出shuffleWriter采用了哪种方式。partitionSpecs则定义了分区规范的类型。
目前在spark 3.2版本中partitionSpecs的实现类主要有以下四个:
CoalescedPartitionSpec分区用于coalesce shuffle partitions 逻辑规则
PartialReducerPartitionSpec参与了skew join 优化
PartialMapperPartitionSpec用于本地随机读取器
CoalescedMapperPartitionSpec用于优化本地随机读取器
不同类型的分区规范其实质是代表不同的随机读取的参数。我们都知道在Spark Shuffle中getReader仅有且唯一的一个实现方式, 即BlockStoreShuffleReader 的实现。但是不同的分区规范意味将给共享的reader器传递不同的参数, 下面是ShuffleRowRDD中的简化代码:
1// ShuffleRowRDD
2override def compute(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[InternalRow] = {
3 val tempMetrics = context.taskMetrics().createTempShuffleReadMetrics()
4 // `SQLShuffleReadMetricsReporter` will update its own metrics for SQL exchange operator,
5 // as well as the `tempMetrics` for basic shuffle metrics.
6 val sqlMetricsReporter = new SQLShuffleReadMetricsReporter(tempMetrics, metrics)
7 val reader = split.asInstanceOf[ShuffledRowRDDPartition].spec match {
8 // CoalescedPartitionSpec会读取map task为所有reducer所产生的shuffle file
9 case CoalescedPartitionSpec(startReducerIndex, endReducerIndex, _) =>
10 SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager.getReader(
11 dependency.shuffleHandle,
12 startReducerIndex,
13 endReducerIndex,
14 context,
15 sqlMetricsReporter)
16 // PartialReducerPartitionSpec 读取map task为一个reducer产生的部分数据
17 case PartialReducerPartitionSpec(reducerIndex, startMapIndex, endMapIndex, _) =>
18 SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager.getReader(
19 dependency.shuffleHandle,
20 startMapIndex,
21 endMapIndex,
22 reducerIndex,
23 reducerIndex + 1,
24 context,
25 sqlMetricsReporter)
26 // PartialMapperPartitionSpec读取shuffle map文件的部分
27 case PartialMapperPartitionSpec(mapIndex, startReducerIndex, endReducerIndex) =>
28 SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager.getReader(
29 dependency.shuffleHandle,
30 mapIndex,
31 mapIndex + 1,
32 startReducerIndex,
33 endReducerIndex,
34 context,
35 sqlMetricsReporter)
36...
37 reader.read().asInstanceOf[Iterator[Product2[Int, InternalRow]]].map(_._2)
38 }CoalescedPartitionSpec(startReducerIndex, endReducerIndex) 分区规范主要是读取map task为所有reducer所产生的shuffle file;PartialReducerPartitionSpec(startMap-Index, endMapIndex,reducerIndex, reducerIndex + 1) 可以看出每次读取只会为一个reducer读取部分数据。
从上面代码可以看出ShuffleRowRDD 使用 read() 方法遍历 shuffle 数据并将其返回给客户端,那么接下来我们就详细的看下getReader是如何实现的?
ShuffleReader调用前的准备
SortShuffleManager是ShuffleManager的唯一实现,里面也实现getReader方法,那么就让我们从getReader开始。
1override def getReader[K, C](
2 handle: ShuffleHandle,
3 startMapIndex: Int,
4 endMapIndex: Int,
5 startPartition: Int,
6 endPartition: Int,
7 context: TaskContext,
8 metrics: ShuffleReadMetricsReporter): ShuffleReader[K, C] = {
9 val baseShuffleHandle = handle.asInstanceOf[BaseShuffleHandle[K, _, C]]
10 val (blocksByAddress, canEnableBatchFetch) =
11 // 是否开启了push-based shuffle, 后续再分享,这里先跳过
12 if (baseShuffleHandle.dependency.shuffleMergeEnabled) {
13 val res = SparkEnv.get.mapOutputTracker.getPushBasedShuffleMapSizesByExecutorId(
14 handle.shuffleId, startMapIndex, endMapIndex, startPartition, endPartition)
15 (res.iter, res.enableBatchFetch)
16 } else {
17 // [1] 使用mapOutputTracker获取shuffle块的位置
18 val address = SparkEnv.get.mapOutputTracker.getMapSizesByExecutorId(
19 handle.shuffleId, startMapIndex, endMapIndex, startPartition, endPartition)
20 (address, true)
21 }
22 // [2] 创建一个BlockStoreShuffleReader实例,该实例将负责将shuffle文件从mapper传递到 reducer 任务
23 new BlockStoreShuffleReader(
24 handle.asInstanceOf[BaseShuffleHandle[K, _, C]], blocksByAddress, context, metrics,
25 shouldBatchFetch =
26 canEnableBatchFetch &&canUseBatchFetch(startPartition, endPartition, context))
27}
可以看到getReader主要做了两件事:
[1] 使用mapOutputTracker获取shuffle块的位置
[2] 创建一个BlockStoreShuffleReader实例,该实例将负责将shuffle文件从mapper传递到reducer 任务
那么Spark中如何保存和获取shuffle块的位置呢?
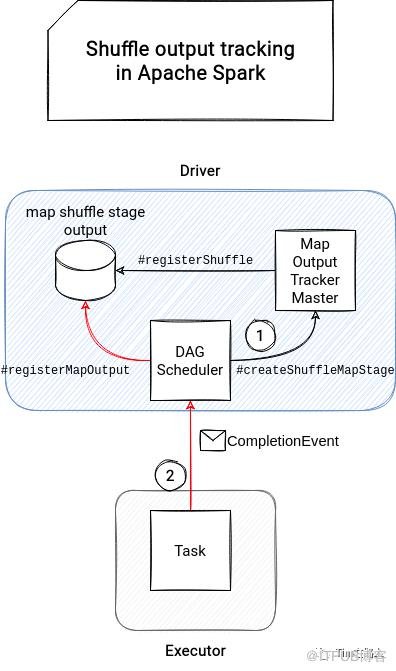
在spark中有两种mapOutputTracker,两种mapOutputTracker 都是在创建SparkEnv时创建。
其中第一个是MapOutputTrackerMaster,它驻留在驱动程序中并跟踪每个阶段的map output输出, 并与DAGScheduler进行通信。
另一个是MapOutputTrackerWorker,位于执行器上,它负责从MapOutputTrackerMaster获取shuffle 元数据信息。
MapOutputTrackerMaster:
DAGScheduler在创建 shuffle map 阶段时会调用registerShuffle方法,从下面的代码可以看出在创建ShuffleMapStage会调用registerShuffle,其实质是在向 shuffleStatuses 映射器中放入shuffleid, 并为其值创建一个新的new ShuffleStatus(numMaps)。
1def createShuffleMapStage[K, V, C](
2 shuffleDep: ShuffleDependency[K, V, C], jobId: Int): ShuffleMapStage = {
3 val rdd = shuffleDep.rdd
4 ...
5 stageIdToStage(id) = stage
6 shuffleIdToMapStage(shuffleDep.shuffleId) = stage
7 updateJobIdStageIdMaps(jobId, stage)
8
9 if (!mapOutputTracker.containsShuffle(shuffleDep.shuffleId)) {
10 // 在创建ShuffleMapStage会调用registerShuffle
11 mapOutputTracker.registerShuffle(shuffleDep.shuffleId, rdd.partitions.length,
12 shuffleDep.partitioner.numPartitions)
13 }
14 stage
15}
16
17def registerShuffle(shuffleId: Int, numMaps: Int, numReduces: Int): Unit = {
18 if (pushBasedShuffleEnabled) {
19 if (shuffleStatuses.put(shuffleId, new ShuffleStatus(numMaps, numReduces)).isDefined) {
20 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Shuffle ID " + shuffleId + " registered twice")
21 }
22 } else {
23 // 可以看到其实质是在向 shuffleStatuses 放入shuffleid, 创建ShuffleStatus
24 if (shuffleStatuses.put(shuffleId, new ShuffleStatus(numMaps)).isDefined) {
25 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Shuffle ID " + shuffleId + " registered twice")
26 }
27 }
28 }
2. 到目前位置master tracker存放了一个shuffleid, 表明DAG中存在一个shuffle, 但还是不知道map output file的具体位置。
1// DAGScheduler中
2private[scheduler] def handleTaskCompletion(event: CompletionEvent): Unit = {
3
4 case smt: ShuffleMapTask =>
5 val shuffleStage = stage.asInstanceOf[ShuffleMapStage]
6 ...
7 mapOutputTracker.registerMapOutput(
8 shuffleStage.shuffleDep.shuffleId, smt.partitionId, status)
9 }
10
11def registerMapOutput(shuffleId: Int, mapIndex: Int, status: MapStatus): Unit = {
12 shuffleStatuses(shuffleId).addMapOutput(mapIndex, status)
13}
从上面代码可以看出,在每次 shuffle map 阶段的任务终止时,DAGScheduler都会向MapOutputTrackerMaster发送状态更新。跟踪器将有关特定 shuffle 文件的位置和大小的信息添加到在注册步骤中初始化 的shuffleStatuses map中。
MapOutputTrackerWorker:
当worker tracker 没有缓存shuffle信息, 这时就必须发送GetMapOutputStatuses消息来从master tracker获取它。
再回过头来看看,在getReader()中通过mapOutputTracker获取shuffle块的位置的方法。
1// mapOutTracker
2private def getMapSizesByExecutorIdImpl(
3 shuffleId: Int,
4 startMapIndex: Int,
5 endMapIndex: Int,
6 startPartition: Int,
7 endPartition: Int,
8 useMergeResult: Boolean): MapSizesByExecutorId = {
9 logDebug(s"Fetching outputs for shuffle$shuffleId")
10 // [1] 获取mapOutputStatuses
11 val (mapOutputStatuses, mergedOutputStatuses) = getStatuses(shuffleId, conf,
12 // EnableBatchFetch can be set to false during stage retry when the
13 // shuffleDependency.shuffleMergeEnabled is set to false, and Driver
14 // has already collected the mergedStatus for its shuffle dependency.
15 // In this case, boolean check helps to insure that the unnecessary
16 // mergeStatus won't be fetched, thus mergedOutputStatuses won't be
17 // passed to convertMapStatuses. See details in [SPARK-37023].
18 if (useMergeResult)fetchMergeResultelse false)
19 ...
20}
从上面可以看出获取具体的map output 位置的实现在getStatuses方法中。下面我们来具体分析下:
1private def getStatuses(
2 shuffleId: Int,
3 conf: SparkConf,
4 canFetchMergeResult: Boolean): (Array[MapStatus], Array[MergeStatus]) = {
5 // push-based shuffle 开启,获取MergeStatus, 现暂不考虑
6 if (canFetchMergeResult) {
7 ...
8 } else {
9 val statuses = mapStatuses.get(shuffleId).orNull
10 // [1] 如果mapStatuses不包含statuses, 就向master tracker发送GetMapOutputStatuses消息
11 if (statuses == null) {
12 logInfo("Don't have map outputs for shuffle " + shuffleId + ", fetching them")
13 val startTimeNs = System.nanoTime()
14fetchingLock.withLock(shuffleId) {
15 var fetchedStatuses =mapStatuses.get(shuffleId).orNull
16 if (fetchedStatuses == null) {
17 logInfo("Doing the fetch; tracker endpoint = " +trackerEndpoint)
18 val fetchedBytes = askTracker[Array[Byte]](GetMapOutputStatuses(shuffleId))
19 try {
20 fetchedStatuses =
21 MapOutputTracker.deserializeOutputStatuses[MapStatus](fetchedBytes, conf)
22 } catch {
23 ...
24 }
25 logInfo("Got the map output locations")
26 mapStatuses.put(shuffleId, fetchedStatuses)
27 }
28 (fetchedStatuses, null)
29 }
30 // [2] 如果mapStatuses包含statuses, 直接返回
31 } else {
32 (statuses, null)
33 }
34 }
35}
从getStatuses可以看出:
[1] 如果mapStatuses不包含statuses, 就向master tracker发送GetMapOutputStatuses消息
[2] 如果mapStatuses包含statuses, 直接返回
1private[spark] sealed trait MapStatus extends ShuffleOutputStatus {
2 def location: BlockManagerId
3
4 def updateLocation(newLoc: BlockManagerId): Unit
5
6 def getSizeForBlock(reduceId: Int): Long
7
8 def mapId: Long
9}
可见MapStatus中包含了location, mapId等信息。
最后,我们再回到getReader()方法中:
通过SparkEnv.get.mapOutputTracker. getMapSizesByExecutorId获取shuffle块信息后,再将其作为 shuffle 块的及其物理位置传递给BlockStoreShuffleReader。那么接下来就我们再来分析下BlockStoreShuffleReader的实现。
为避免冗长将BlockStoreShuffleReader放到下一讲进行分析。