BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter 就如其名,旁支的sort-baesd Shuffle, 他是采用Hash-style实现的Sort based Shuffle。在map阶段records会按分区写入不同的文件, 一个分区一个文件。然后链接这些分区文件形成一个output文件,并生成其index。reducer通过IndexShuffleBlockResolver查找消费输出文件的不同分区。
在 BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter 中records是不会缓存在内存中,所有的records最终都会被flush到磁盘。
在写入时,BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter 会同时为所有的分区打开单独的序列化器和文件流,所以当reduce分区数量特别大的时候性能会非常低下。
ShuffleWriter 的调用是在ShuffleMapTask的runTask中进行调用,每个mapTask 都会调用一次runTask。
BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter 源码解析
首先,我们来回顾下ShuffleWriter的过程。Shuffle发生与宽依赖的stage间,由于stage内的计算采用pipeline的方式。shuffle发生的上一个stage为map节点,下游的stage为reduce阶段。而shuffle写的过程就发生在map阶段,shuffleWriter的调用主要是在ShuffleMapStage中,每个ShuffleMapStage包含多个ShuffleMapTask, mapTask个数和分区数相关。
这样每个ShuffleMapTask都会在其runTask调用下Writer接口,其并非直接调用到具体的执行类。而是在划分宽依赖时会获取ShuffleManage,并注册shuffle,这时会返回的具体ShuffleHandler。
在ShuffleMapTask调用Writer时,是先调用了ShuffleWriteProcessor ,主要控制了ShuffleWriter的生命周期。下面我们看下ShuffleWriteProcessor 中的Write的实现:
1// ShuffleWriteProcessor
2def write(
3 rdd: RDD[_],
4 dep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _],
5 mapId: Long,
6 context: TaskContext,
7 partition: Partition): MapStatus = {
8 var writer: ShuffleWriter[Any, Any] = null
9 try {
10 // [1] 通过SparkEnv获取ShuffleManager, 并通过dep的shuffleHandle, 获取对应的shuffleWriter的具体实现。
11 val manager = SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager
12 writer = manager.getWriter[Any, Any](
13 dep.shuffleHandle,
14 mapId,
15 context,
16 createMetricsReporter(context))
17 // [2] 调用shuffleWriter的write方法, 并将当前rdd的迭代器传入
18 writer.write(
19 rdd.iterator(partition, context).asInstanceOf[Iterator[_ <: Product2[Any, Any]]])
20 // [3] shuffleWriter结束后,返回mapStatus,或清空数据
21 val mapStatus = writer.stop(success = true)
22 // [4] 如果shuffleWriter执行成功,初始化push-based shuffle, 后面再细讲
23 if (mapStatus.isDefined) {
24 // Initiate shuffle push process if push based shuffle is enabled
25 // The map task only takes care of converting the shuffle data file into multiple
26 // block push requests. It delegates pushing the blocks to a different thread-pool -
27 // ShuffleBlockPusher.BLOCK_PUSHER_POOL.
28 if (dep.shuffleMergeEnabled && dep.getMergerLocs.nonEmpty && !dep.shuffleMergeFinalized) {
29 manager.shuffleBlockResolver match {
30 case resolver: IndexShuffleBlockResolver =>
31 val dataFile = resolver.getDataFile(dep.shuffleId, mapId)
32 new ShuffleBlockPusher(SparkEnv.get.conf)
33 .initiateBlockPush(dataFile, writer.getPartitionLengths(), dep, partition.index)
34 case _ =>
35 }
36 }
37 }
38 mapStatus.get
39 }
40...
41}
ShuffleWriteProcessor 中主要做了三件事:
[1] 通过SparkEnv获取ShuffleManager, 并通过dep的shuffleHandle, 获取对应的shuffleWriter的具体实现。
[2] 调用shuffleWriter的write方法, 并将当前rdd的迭代器传入
[3] shuffleWriter结束后,返回mapStatus,或清空数据
可见每一个ShuffleMapTask执行结束后,就会返回一个mapStatus。Task 结果被封装成 CompletionEvent发送到Driver DAG Scheduler 。判断Task的类型是ShuffleMapTask,DagScheduler 会向 MapOutputTracker 注册 MapOutput status 信息。
那么map中的数据是如何通过BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter写入的?
1// BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter
2@Override
3public void write(Iterator> records) throws IOException {
4 assert (partitionWriters == null);
5 // [1] 创建处理mapTask所有分区数据commit提交writer
6 ShuffleMapOutputWriter mapOutputWriter = shuffleExecutorComponents
7 .createMapOutputWriter(shuffleId, mapId, numPartitions);
8 try {
9 // 如果没有数据,直接提交所有分区的commit, 并返回分区长度,获取mapStatus
10 if (!records.hasNext()) {
11 partitionLengths = mapOutputWriter.commitAllPartitions(
12 ShuffleChecksumHelper.EMPTY_CHECKSUM_VALUE).getPartitionLengths();
13 mapStatus = MapStatus$.MODULE$.apply(
14 blockManager.shuffleServerId(), partitionLengths, mapId);
15 return;
16 }
17 final SerializerInstance serInstance = serializer.newInstance();
18 final long openStartTime = System.nanoTime();
19 // [2] 为每个分区创建一个DiskBlockObjectWriter写入流和FileSegment文件段
20 partitionWriters = new DiskBlockObjectWriter[numPartitions];
21 partitionWriterSegments = new FileSegment[numPartitions];
22 for (int i = 0; i < numPartitions; i++) {
23 // [2.1] 每个分区创建个临时file和blockid, 并生成维护一个写入流
24 final Tuple2 tempShuffleBlockIdPlusFile =
25 blockManager.diskBlockManager().createTempShuffleBlock();
26 final File file = tempShuffleBlockIdPlusFile._2();
27 final BlockId blockId = tempShuffleBlockIdPlusFile._1();
28 DiskBlockObjectWriter writer =
29 blockManager.getDiskWriter(blockId, file, serInstance, fileBufferSize, writeMetrics);
30 if (partitionChecksums.length > 0) {
31 writer.setChecksum(partitionChecksums[i]);
32 }
33 partitionWriters[i] = writer;
34 }
35 // Creating the file to write to and creating a disk writer both involve interacting with
36 // the disk, and can take a long time in aggregate when we open many files, so should be
37 // included in the shuffle write time.
38 writeMetrics.incWriteTime(System.nanoTime() - openStartTime);
39 // [3] 依次将records写入到对应分区的写入流中, 并提交
40 while (records.hasNext()) {
41 final Product2 record = records.next();
42 final K key = record._1();
43 partitionWriters[partitioner.getPartition(key)].write(key, record._2());
44 }
45
46 // [3.1]依次对每个分区提交和flush写入流
47 for (int i = 0; i < numPartitions; i++) {
48 try (DiskBlockObjectWriter writer = partitionWriters[i]) {
49 partitionWriterSegments[i] = writer.commitAndGet();
50 }
51 }
52 // [4] 遍历所有分区的FileSegement, 并将其链接为一个文件,同时会调用writeMetadataFileAndCommit,为其生成索引文件
53 partitionLengths = writePartitionedData(mapOutputWriter);
54 mapStatus = MapStatus$.MODULE$.apply(
55 blockManager.shuffleServerId(), partitionLengths, mapId);
56 } catch (Exception e) {
57 try {
58 mapOutputWriter.abort(e);
59 } catch (Exception e2) {
60logger.error("Failed to abort the writer after failing to write map output.", e2);
61 e.addSuppressed(e2);
62 }
63 throw e;
64 }
65}
综上,Bypass的writer步骤有四步:
[1] 创建处理mapTask所有分区数据commit提交writer
[2] 为每个分区创建一个DiskBlockObjectWriter写入流和FileSegment文件段
[2.1] 每个分区创建个临时file和blockid, 并生成维护一个DiskBlockObjectWriter写入流[3] 依次将records写入到对应分区的写入流中, 并提交
[3.1]依次对每个分区提交和flush写入流[4] 遍历所有分区的FileSegement, 并将其链接为一个文件,同时会调用writeMetadataFileAndCommit,为其生成索引文件
所以说, Bypass在进行写入时会为每个MapTask都会生成reduce分区个FileSegement, 写入时会并发的为所有的分区都创建临时文件和维护一个io的写入流, 最终在链接为一个文件。所以如果分区数特别多的情况下,是会维护很多io流,所以Bypass限制了分区的阈值。另外通过源码发现Bypass在实现过程中并没有使用buffer, 而是直接将数据写入到流中,这也就是为什么Bypass不能处理mapSide的预聚合的算子。
那么BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter 属于sort-based Shuffle 到底有没有排序呢?
接下来,我们再看下Bypass是如何将分区的FileSegement, 并将其链接为一个文件, 我们就需要详细看下writePartitionedData是如何实现的。
1private long[] writePartitionedData(ShuffleMapOutputWriter mapOutputWriter) throws IOException {
2 // Track location of the partition starts in the output file
3 if (partitionWriters != null) {
4 final long writeStartTime = System.nanoTime();
5 try {
6 for (int i = 0; i < numPartitions; i++) {
7 // [1] 获取每个分区的 fileSegement 临时文件,和writer写出流
8 final File file = partitionWriterSegments[i].file();
9 ShufflePartitionWriter writer = mapOutputWriter.getPartitionWriter(i);
10 if (file.exists()) {
11 if (transferToEnabled) {
12 // Using WritableByteChannelWrapper to make resource closing consistent between
13 // this implementation and UnsafeShuffleWriter.
14 Optional maybeOutputChannel = writer.openChannelWrapper();
15 if (maybeOutputChannel.isPresent()) {
16 writePartitionedDataWithChannel(file, maybeOutputChannel.get());
17 } else {
18 writePartitionedDataWithStream(file, writer);
19 }
20 } else {
21 // [2] 将fileSegement合并为一个文件
22 writePartitionedDataWithStream(file, writer);
23 }
24 if (!file.delete()) {
25logger.error("Unable to delete file for partition {}", i);
26 }
27 }
28 }
29 } finally {
30 writeMetrics.incWriteTime(System.nanoTime() - writeStartTime);
31 }
32 partitionWriters = null;
33 }
34 // [3] 提交所有的分区,传入每个分区数据的长度, 调用 writeMetadataFileAndCommit生成索引文件,记录每个分区的偏移量
35 return mapOutputWriter.commitAllPartitions(getChecksumValues(partitionChecksums))
36 .getPartitionLengths();
37}
writePartitionedData是如何实现,有三个步骤:
[1] 获取每个分区的 fileSegement 临时文件,和writer写出流
[2] 将fileSegement合并为一个文件
[3] 提交所有的分区,传入每个分区数据的长度, 调用 writeMetadataFileAndCommit生成索引文件,记录每个分区的偏移量
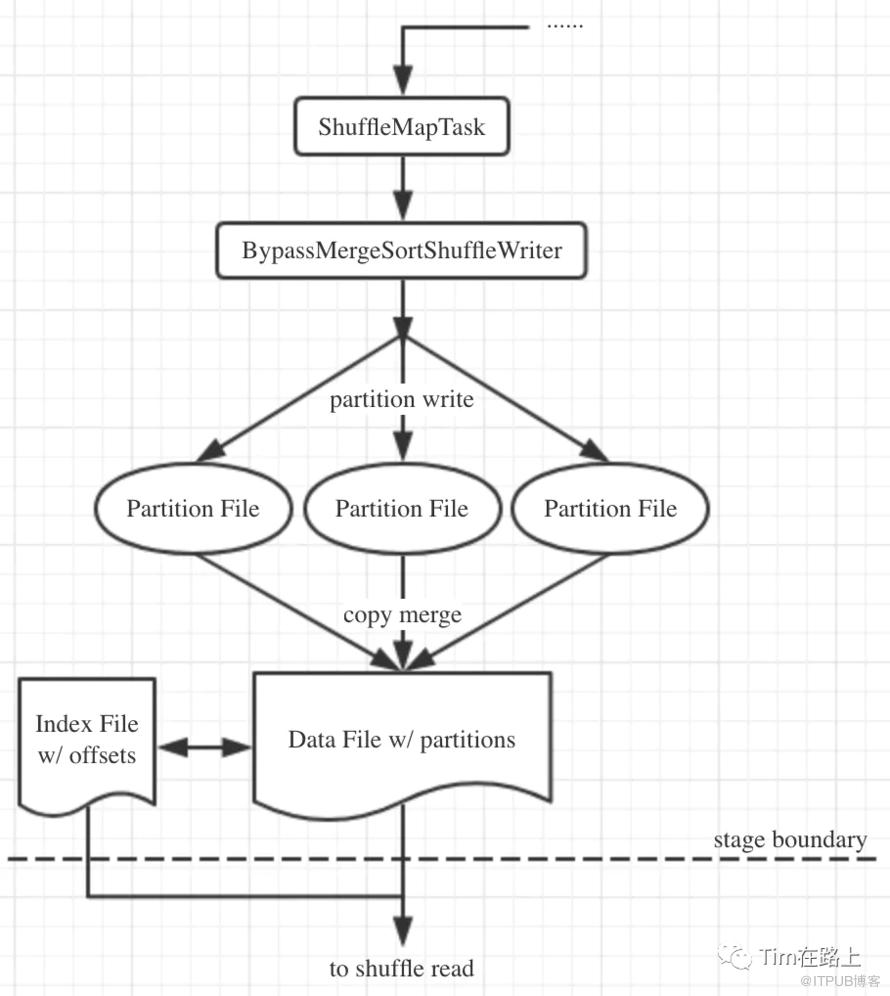
总结, BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter 的实现是hash-style的方式,其中没有sort, 没有buffer,每一个mapTask都会生成分区数量个FileSegment, 最后再合并为一个File, 最终根据分区的长度为其生成索引文件。所以BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter在分区数量比较小的情况下,性能是比较佳的。其最终每个task会生成2个文件, 所以最终的生成文件数也是2 * M个文件。
今天就先到这里,通过上面的介绍,我们也留下些面试题:
BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter和HashShuffle有什么区别?
为什么不保留HashShuffleManage, 而是将其作为SortShuffleManager中的一个Writer实现?